
Written by Yoga Mentor Keshav, with facts sourced from Ancient Indian Ayurvedic and Yogic Textbooks, as well as scientific research.
Eggs are a common food that many people enjoy because of its high nutritional value. While it’s widely believed that eggs are a powerhouse of proteins, the reality is a bit different. Contrary to the myth, eggs are not solely dominated by protein.
However, there are several evidence-based reasons to consider before you have this popular food.
Let’s explore some common egg myths versus the reality to make informed choices to have eggs or not to have eggs.
Egss are often considered as a complete source of protein but they might not reign supreme in the nutritional arena! Let’s take a closer look:
| Food | Nutritional Value per 100g |
|---|---|
| Egg (boiled) | Calories (155), Protein (12.6 g), Fat (10.6 g), Carbohydrates (0.23 g), Fiber (0 g), Magnesium (10 mg), Zinc (0.7 mg), Choline (294 mg), Calcium (50 mg), Iron (1.94 mg) |
| Moong (Boiled) | Calories (105), Protein (7 g), Fat (6 g), Carbohydrates (19.2 g), Fiber (7.6 g), Magnesium (48 mg), Zinc (0.84 mg), Choline (29.4 mg), Calcium (27 mg), Iron (1.4 mg) |
| Rajma (Cooked) | Calories (127), Protein (8.67 g), Fat (1 g), Carbohydrates (22.8 g), Fiber (6.4 g), Magnesium (42 mg), Zinc (1 mg), Choline (30.5 mg), Calcium (35 mg), Iron (2.2 mg) |
| Quinoa (Cooked) | Calories (120), Protein (4.4 g), Fat (1.9 g), Carbohydrates (21.3 g), Fiber (2.8 g), Magnesium (48 mg), Zinc (1.09 mg), Choline (23 mg), Calcium (17 mg), Iron (1.5 mg) |
| Coriander Seeds (Raw) | Calories (298), Protein (12.4 g), Fat (17.8 g), Carbohydrates (55 g), Fiber (41.9 g), Magnesium (330 mg), Zinc (4.7 mg), Choline (0 mg), Calcium (709 mg), Iron (16.3 mg) |
| Flax Seeds (Raw) | Calories (534), Protein (18.3 g), Fat (42 g), Carbohydrates (28.9 g), Fiber (27.3 g), Magnesium (392 mg), Zinc (4.34 mg), Choline (78.7 mg), Calcium (255 mg), Iron (5.73 mg) |
| Chia Seeds (Raw) | Calories (486), Protein (16.5 g), Fat (30.9 g), Carbohydrates (42.1 g), Fiber (37.4 g), Magnesium (27 mg), Zinc (2.7 mg), Choline (55 mg), Calcium (187 mg), Iron (1.8 mg) |
| Sprouts of Moong | Calories (30), Protein (3.04 g), Fat (0.18 g), Carbohydrates (5.94 g), Fiber (1.8 g), Magnesium (21 mg), Zinc (0.41 mg), Choline (14.4 mg), Calcium (13 mg), Iron (0.91 mg) |
Protein Facts: Flax Seeds (18.3 g) and Chia Seeds (16.5 g) have higher protein compared to eggs (12.6g), respectively, making them excellent plant-based alternatives for muscle building and repair.
Fiber : Chia Seeds & Coriander Seeds are excellent sources. Egg has no fiber which is crucial for aiding digestion and promoting gut health.
Fat Facts: Chia Seeds and Coriander Seeds deliver healthy fats like omega-3s and monounsaturated fats, while Rajma keeps it light on fat content.
Check your Daily Protein Intake Here!
Calcium : Flax Seeds and Coriander Seeds double the calcium of eggs, crucial for strong bones and teeth.
Magnesium: Flax Seeds (392 mg) are a powerhouse of magnesium. Eggs significantly lower in magnesium than Flax Seeds & Coriander Seeds, vital for muscle function and energy production.
Iron : Eggs lower in iron than Coriander Seeds (742% more). advantage over eggs (1.94 mg), crucial for oxygen transport and red blood cell production.
Egg allergies are one of the most common food allergies in children, affecting up to 2% of children under the age of 3. Egg allergies can cause a variety of symptoms, including hives, eczema, swelling, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis. In some cases, egg allergies can persist into adulthood. Evidence.
Egg allergies are caused by an overreaction of the immune system to egg proteins. When a person with an egg allergy eats eggs, their immune system produces antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE).

These antibodies bind to egg proteins and trigger the release of histamine, a chemical that causes allergic symptoms.
The severity of egg allergies can vary from person to person. Some people with egg allergies may be able to tolerate small amounts of eggs without experiencing any symptoms, while others may experience a severe allergic reaction even to a small amount of exposure.
People with egg allergies should avoid eating eggs and any foods that contain eggs. They should also be aware of the risk of cross-contamination, which occurs when eggs come into contact with other foods.
Eggs have a lot of cholesterol – one boiled/cooked/hard boiled egg (100 gm) has about 373 milligrams. That’s more than half of what experts say is okay for adults to have in a whole day. Evidence.
Check your Body Fat with Body Fat Calculator Here !
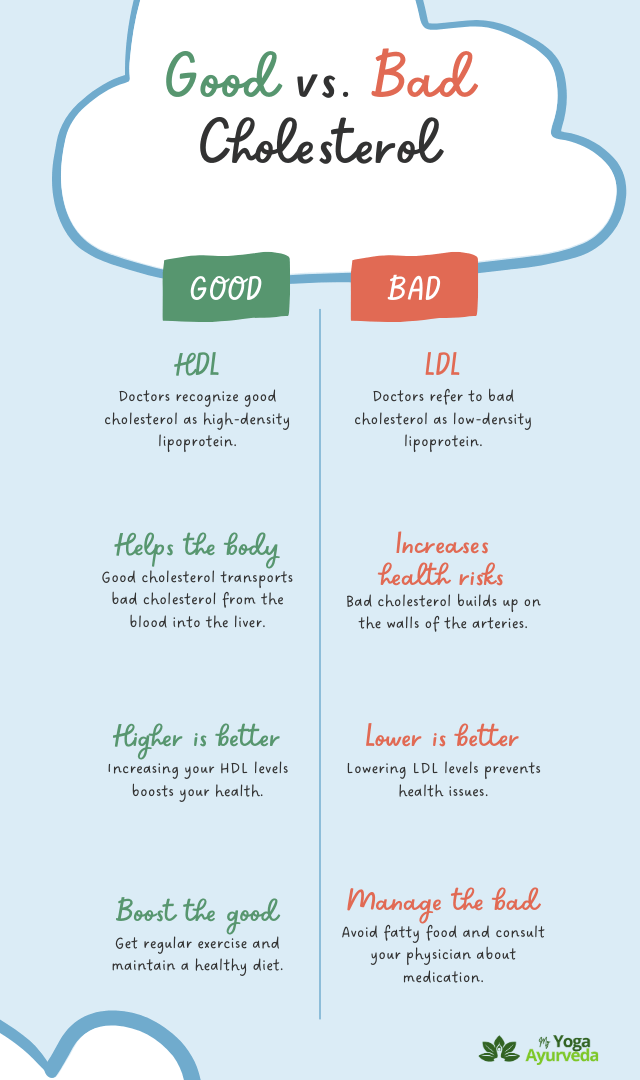
Cholesterol is a waxy thing in all animal cells. It helps make hormones and cell walls in our bodies.
But if we have too much cholesterol, it might make us more likely to have heart problems or a stroke.
Let’s see what is good and bad cholesterol.
Read this Also : How to Keep your Heart Healthy
The American Heart Association suggests that for a healthy heart, adults should have no more than 300 milligrams of cholesterol per day.
If you have high cholesterol, heart disease, or diabetes, it’s even better to keep your daily cholesterol intake to 200 milligrams or less.
If you’re worried about the cholesterol you eat, it’s a good idea to avoid eating too many eggs.
There might be a link between eating eggs and an increased risk of cancer-related mortality. Evidence.
The reasons behind this association could be:
Gallbladder Contraction: Egg yolk could lead to more frequent contractions of the gallbladder, causing an increased release of bile acids into the intestine. Bile acids have been associated with causing gastrointestinal cancer.
High Choline Content: Eggs contain a lot of choline, a nutrient essential for cell functions related to cancer growth and progression.
Cholesterol Disruption: Eggs, combined with aging and cancer cells, may disrupt the balance of cholesterol in the body.
This disruption could lead to the accumulation of cholesterol, acting as a precursor for the production of androgen (a male sex hormone) and affecting signaling pathways that promote cancer progression.
Eggs can contain residues of veterinary drugs, such as antibiotics and hormones. These drugs are used to treat and prevent diseases in chickens.
However, they can also be harmful to humans, especially children and pregnant women.
A study was conducted in Chittagong (Bangladesh) from December 2011 to June 2012 to detect and measure the levels of antibiotic residues in both milk and eggs from local and commercial farms. It found that there were higher level of antibiotic residues in Eggs Evidence.
The dangers of antibiotics used by poultry industries in poultry eggs is well known. The danger of having antibiotics in eggs is more significant in developing countries compared to developed ones.
Antibiotic residues in eggs can pose a number of health risks to humans. They can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance, which can make it difficult to treat infections. Antibiotic residues can also cause allergic reactions in some people.
Salmonella is a kind of bacteria that can make you sick with food poisoning. Eggs can become contaminated with salmonella during production, transportation, or storage.
Salmonella can cause a variety of symptoms, including diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and cramps. In severe cases, salmonella can lead to death.
To reduce the risk of salmonella infection, it is important to cook eggs thoroughly. Eggs should be cooked until the yolks are firm and the whites are set.
It is also important to wash your hands thoroughly after handling eggs and to avoid cross-contamination.
Studies suggest that regularly eating eggs might not be the best idea, especially for people dealing with cancer, heart disease, or diabetes.
It’s also important to look into how eggs are cooked and explore other protein options.
If you are concerned about any of these risks, you may want to consider avoiding eggs. There are many other healthy and nutritious foods that you can eat instead.
Now it is for you to decide what you want to have Eggs or Vegetarian foods such as Samak Rice in your diet.


