
Written by Yoga Mentor Keshav, with facts sourced from Ancient Indian Ayurvedic and Yogic Textbooks, as well as scientific research.
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is a fat-soluble vitamin that is naturally produced in the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D is also obtained through certain foods and supplements. It is known for its role in promoting calcium absorption and bone health. Additionally, vitamin D supports immune function and helps regulate cell growth and differentiation.
Vitamin D is a group of compounds that includes vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). These compounds are converted into their active form in the body and have important functions in maintaining health.
Vitamin D is crucial for the regulation of calcium and phosphorus absorption, which are essential for the development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth. It also plays a role in modulating cell growth, immune function, and reducing inflammation.
Vitamin D acts as a hormone in the body, influencing the functioning of various systems.
Its primary role is in regulating calcium levels in the blood, promoting the absorption of calcium from the intestines and reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys.
This helps maintain adequate calcium concentrations for normal bone mineralization, muscle function, and nerve transmission.
Vitamin D also plays a role in cell growth, immune system modulation, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain cancers.

The main source of vitamin D is sunlight.
When the skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation from sunlight, a precursor compound in the skin is converted into vitamin D3.
This form of vitamin D is then further metabolized in the liver and kidneys to its active form.
In addition to sunlight, vitamin D can be obtained from certain foods.
Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and sardines are excellent sources of vitamin D.
Cod liver oil is another rich source.
Other food sources include egg yolks, fortified milk and dairy products, fortified cereals, and some plant-based milk alternatives.
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin D is as follows:
It is important to note that individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin tones, older adults, and those with certain medical conditions may require higher levels of vitamin D supplementation.
Vitamin D is primarily absorbed through the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
Within the epidermis, the absorption of vitamin D occurs when UVB rays from sunlight penetrate the skin.
More specifically, a cholesterol compound present in the skin called 7-dehydrocholesterol is converted into previtamin D3 when exposed to UVB radiation.
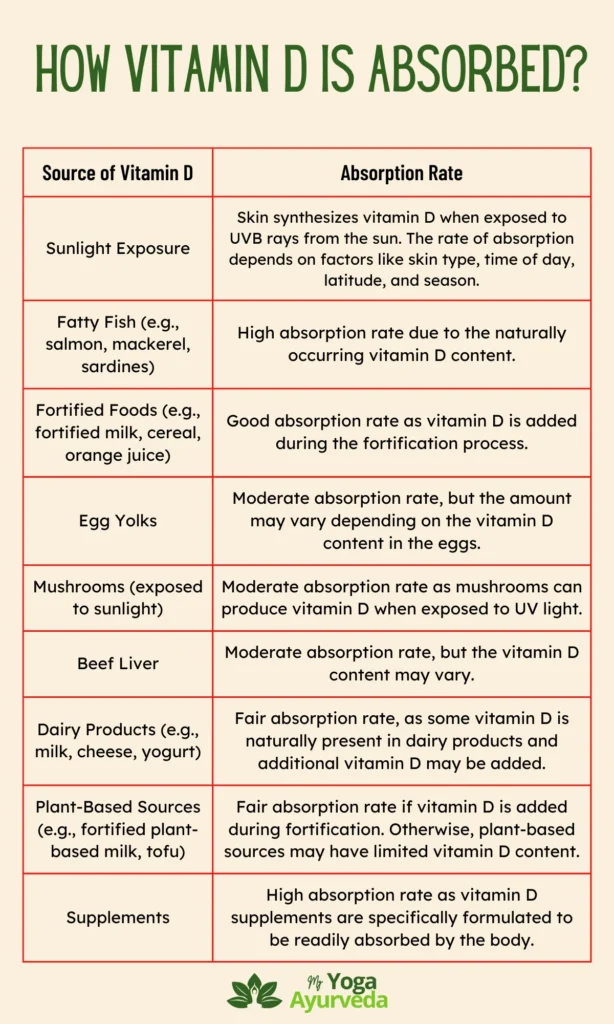
This previtamin D3 is then converted into active vitamin D (calcitriol) through a process involving the liver and kidneys.
It’s worth noting that the amount of vitamin D produced depends on the amount of exposed skin and the intensity of sunlight.
Exposing larger areas of skin, such as the arms, legs, and back, to sunlight can enhance the absorption and synthesis of vitamin D.
However, it’s important to maintain a balance between sun exposure and the risk of sunburn or skin damage.
Sunlight as the Primary Source of Vitamin D. Sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D for most individuals. When the skin is exposed to UVB radiation from the sun, a chemical reaction occurs, converting a precursor compound in the skin to vitamin D3.
This form of vitamin D is then further metabolized in the liver and kidneys to its active form, which can be utilized by the body.
It is recommended to spend a limited amount of time in the sun, especially during peak hours, and to use sun protection measures such as wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a sufficient sun protection factor (SPF), and seeking shade when necessary.
Natural Food Sources of Vitamin D
In addition to sunlight exposure, vitamin D can be obtained from various food sources.
Fatty Fish (e.g., Salmon, Tuna, Sardines)
Fatty fish are among the richest dietary sources of vitamin D. Species such as salmon, tuna, and sardines contain high levels of vitamin D3. Including these fish in your diet can help increase your vitamin D intake.
Cod Liver Oil
Cod liver oil is derived from the liver of codfish and is a concentrated source of vitamin D. It has been traditionally used as a supplement to provide vitamin D and other essential nutrients.
Egg Yolks
Egg yolks also contain small amounts of vitamin D. However, the vitamin D content may vary depending on the diet of the hens. Eggs from chickens raised on a diet enriched with vitamin D or fed a diet rich in insects and greens may have higher levels of vitamin D.
Fortified Food Products
To address the challenge of obtaining sufficient vitamin D from natural food sources, some food products are fortified with vitamin D.
Milk and Dairy Alternatives
Many brands of cow’s milk and dairy alternatives such as soy milk and almond milk are fortified with vitamin D. Check the labels to ensure you are purchasing products that have been fortified with vitamin D.
Cereals and Breakfast Bars
Certain breakfast cereals and granola bars are fortified with vitamin D. These products can provide a convenient way to incorporate vitamin D into your diet, especially for those who may have dietary restrictions or preferences.
Orange Juice and Soy Milk
Some brands of orange juice and soy milk are fortified with vitamin D, offering additional options for individuals looking to increase their vitamin D intake.
Supplements
In cases where sunlight exposure and dietary sources are insufficient, vitamin D supplements can be used to meet the recommended daily intake.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and type of supplement based on individual needs.
Importance of Vitamin D for Bone Health
One of the key roles of vitamin D is in promoting calcium absorption and maintaining optimal bone health.
Calcium Absorption and Bone Density
Vitamin D enhances the absorption of calcium from the intestine into the bloodstream. It helps maintain proper calcium levels, which are essential for bone mineralization and maintaining bone density.
Adequate vitamin D levels contribute to stronger bones and teeth, reducing the risk of conditions such as osteoporosis and fractures.
Prevention of Osteoporosis and Fractures
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased vulnerability to fractures.
Vitamin D, along with calcium, plays a crucial role in preventing osteoporosis by promoting optimal bone health.
Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin D throughout life can contribute to the prevention of osteoporosis and reduce the risk of fractures, especially in older adults.
Immune System Support
Vitamin D also plays a role in supporting the immune system and overall immune function.
Regulation of Immune Response
Vitamin D is involved in modulating the immune response, including the activation and function of immune cells.
It helps regulate the production of certain proteins and peptides involved in immune defense mechanisms.
Adequate vitamin D levels are believed to enhance immune response and help protect against infections and autoimmune disorders.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research suggests that maintaining optimal vitamin D levels may be associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Adequate vitamin D intake has been linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension and heart disease, as well as type 2 diabetes.
Vitamin D may also play a role in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, although more studies are needed to establish a definitive link.
Mental Health and Vitamin D
Emerging evidence suggests a potential link between vitamin D and mental health.
Depression and Mood Disorders
Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of depression and other mood disorders.
Vitamin D receptors are present in areas of the brain involved in mood regulation, and deficiency may impact neurotransmitter function.
While more research is needed to establish a causal relationship, maintaining adequate vitamin D levels may play a role in supporting mental well-being.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs in certain seasons, typically during fall and winter when sunlight exposure is limited.
The reduced sunlight during these seasons can lead to vitamin D deficiency, which may contribute to the development of SAD. Ensuring sufficient vitamin D levels, particularly during darker months, may help alleviate symptoms of SAD.
Vitamin D Benefits in Cardiovascular Health
Research suggests that vitamin D may play a role in promoting cardiovascular health. Adequate vitamin D levels may help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of hypertension.
Some studies have found an association between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of heart disease, including heart attack and stroke. However, more research is needed to establish a causal relationship.
Type 2 Diabetes
Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels may be beneficial in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Vitamin D is involved in insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for the regulation of blood sugar levels.
Vitamin D may help reduce inflammation, which is linked to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
Cancer Prevention
While the relationship between vitamin D and cancer prevention is still being studied, there is evidence suggesting a potential protective effect. Adequate vitamin D levels may be associated with a lower risk of colon cancer.
Some studies have found an inverse association between vitamin D levels and the risk of breast and prostate cancer.
However, more research is needed to establish definitive conclusions.
While sunlight exposure is important for vitamin D synthesis, it is essential to balance the benefits with the risks of sunburn and skin cancer. Practice safe sun habits by wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and sunglasses, especially during prolonged exposure or when the sun is strongest.
Interactions with Medications
Vitamin D supplements can interact with certain medications, including corticosteroids, anticonvulsants, and some cholesterol-lowering drugs.
If you are taking any medications, it is important to discuss potential interactions with your healthcare provider before starting vitamin D supplementation.
Individual Variations and Medical Conditions
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, may have specific considerations regarding vitamin D intake. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.
How much vitamin D do I need daily?
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. Generally, infants up to 12 months require 400 IU (International Units) per day, while children and adults up to age 70 require 600-800 IU per day. Individuals over 70 may need 800-1,000 IU per day. It is best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Can I get enough vitamin D from sunlight alone?
While sunlight exposure is an important source of vitamin D, it may not be sufficient for everyone, especially during certain seasons or for those with limited sun exposure.
Dietary sources and supplements may be necessary to meet the recommended daily intake.
Can I overdose on vitamin D?
Excessive intake of vitamin D can lead to toxicity, known as vitamin D toxicity or hypervitaminosis D. This usually occurs with extremely high doses of vitamin D supplements and not through sunlight exposure or dietary sources.
It is important to follow the recommended daily intake guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional before taking high-dose vitamin D supplements.
Can you get enough vitamin D from sunlight alone?
While sunlight is a primary source of vitamin D, several factors can affect its synthesis in the body. These include skin pigmentation, geographic location, time of year, and sun protection measures.
Depending on these factors, it may be challenging to obtain sufficient vitamin D solely from sunlight. Therefore, a combination of sunlight exposure, dietary sources, and supplements, if necessary, is recommended.
What are the risks of excessive vitamin D intake?
Excessive vitamin D intake can lead to a condition called hypervitaminosis D. This can result in symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, excessive thirst, frequent urination, and even kidney problems.
It is important to follow the recommended daily intake guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional before taking high-dose vitamin D supplements.
Can vitamin D deficiency cause bone problems?
Yes, vitamin D deficiency can lead to bone problems such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
These conditions weaken the bones, making them more susceptible to fractures and deformities. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is essential for proper bone health and prevention of such conditions.


